What are gas fees, and why does a transaction cost so much? What is a Gwei and why do I have to pay it? Read on to find the answers to these questions and more.
December 6th 2021| Mike Humphrey
Table of Contents
What is Gas in Crypto

What is Gwei
If you have ever created a transaction on Ethereum, you may have noticed that gas prices are shown in Gwei. Gwei is the smallest possible unit of Ethereum. 1 Gwei is equal to 0.000000001Eth or 10^(-9) Eth. Conversely 1 Eth is the equivalent of 1 billion Gwei. Gwei is a useful denomination for calculating Ethereum gas prices.
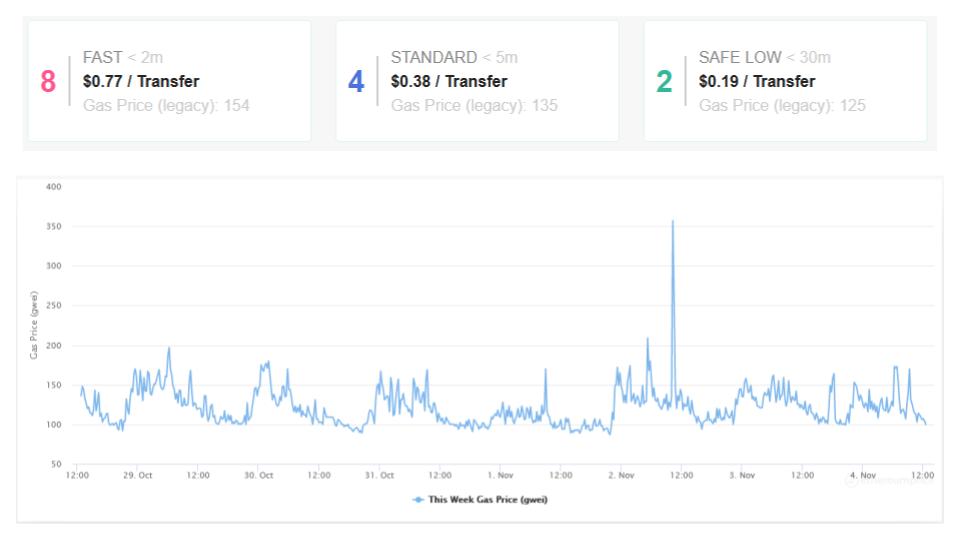
How to Check Ethereum Gas Prices
Before sending a transaction, you may want to check the current gas prices. There are several websites that monitor the current and historical gas prices on the Ethereum network. If you are performing transactions on the Ethereum mainnet where fees can be quite high it’s worthwhile looking for optimal time windows.
Metamask Gas Fee Settings
When performing a transaction using a Metamask wallet, the gas fees are automatically chosen for you. To modify the recommended rates click on edit above the gas fees in the approval window.
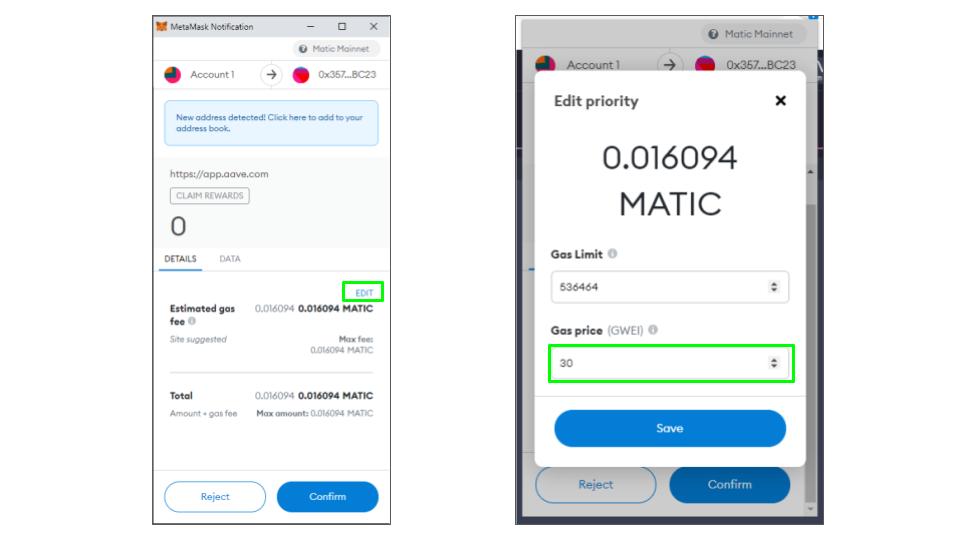
If you are going to decrease the gas price, it’s recommended that you double check one of the sites above, to see whether your settings are too low. Network congestion and low fees are causes of stuck transfers. If you have set your gas price too low, your may have to fix a stuck transaction.
FAQ
Why Are Ethereum Gas Prices So High?
Ethereum gas prices fluctuate based on demand. The more people looking to perform transactions at the same time, the higher the gas price. If you are looking for lower gas prices, try using Etheruem during non-peak hours, or look at using one of the many layer 2 options. Layer 2 solutions use different techniques to lower prices and increase speeds. Polygon, Avalanche, Fantom and Optimism are several of the many solutions currently available. Thinking of moving to Polygon, read our Polygon Bridging Guide.
What is ETH 2.0 and will it decrease gas fees?
Eth 2.0 is the transition of Ethereum from Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS). Proof of Work requires crypto miners to use computers to solve mathematical equations in order to validate the block chain. Proof of Stake on the other hand validates transactions with staked Ethereum. The transition to Eth 2.0 is expected to decrease gas fees. Validators will no longer have to pay for energy intensive mining, which reduces the cost required to validate transactions. This being said, currently there is only a small portion of Eth staked, and there will likely be a spike in gas fees during the transition, until sufficient Eth has been staked. Like PoW, supply and demand will dictate the amount of Eth staked vs gas fees. As demand increases high gas fees will be paid, which increases the return on staked Eth, making staking a more attractive investment.
Have you staked an Ether? Let us know in the comments
Hi I’m Mike, an active crypto investor DeFi enthusiast and crypto miner. I have been involved in crypto since March of 2021 and in DeFi since May 2021.
I’m also an avid outdoor adventurer!